Introduction: Why Risk Management Is Critical for GenAI in Enterprises
Gen AI services adoption is accelerating across industries, from banking and healthcare to manufacturing and retail. While the potential benefits are substantial, enterprises face significant risks—including regulatory non-compliance, data breaches, intellectual property exposure, and ethical concerns.
A GenAI Risk Management & Compliance Framework ensures that generative AI initiatives are safe, secure, and aligned with corporate policies and regulations, enabling enterprises to scale innovation responsibly.
What Is a GenAI Risk Management & Compliance Framework?
A GenAI risk management framework is a structured approach to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks associated with generative AI initiatives. It addresses:
- Regulatory compliance: GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations
- Data privacy and security: Protecting sensitive and proprietary information
- Intellectual property (IP): Avoiding unauthorized content or copyright violations
- Ethical AI practices: Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability
- Operational risks: Model inaccuracies, hallucinations, or workflow failures
By integrating risk management into the AI lifecycle, enterprises reduce exposure while enabling confident adoption.
Why Traditional Risk Management Falls Short for GenAI
Generative AI presents unique challenges not covered by traditional IT or operational risk frameworks:
- Non-deterministic outputs and hallucinations
- Rapidly evolving foundation models and vendors
- Increased reliance on data-driven decisions
- Ethical, regulatory, and reputational implications
A specialized framework ensures that these risks are identified, quantified, and mitigated proactively.
Core Components of a GenAI Risk Management & Compliance Framework
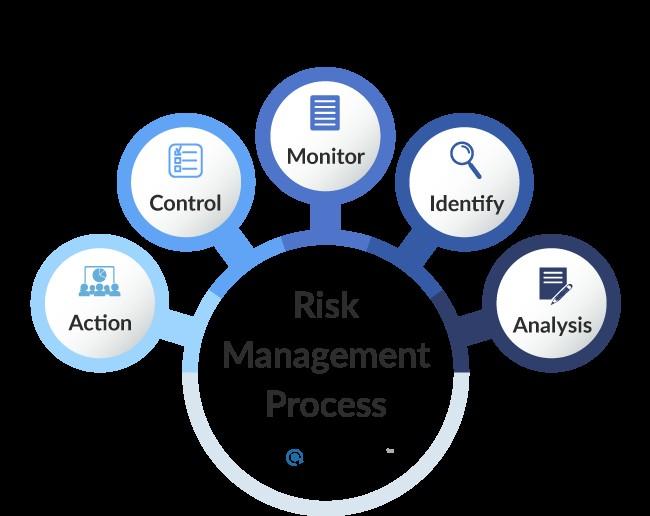
1. Risk Identification
Identify potential risks across GenAI initiatives, including:
- Model performance failure
- Data privacy breaches
- Bias and fairness violations
- Intellectual property misuse
- Regulatory non-compliance
This step establishes a clear risk landscape for the enterprise.
2. Risk Assessment & Prioritization
Evaluate each risk in terms of:
- Likelihood of occurrence
- Business impact
- Compliance or legal consequences
- Reputational exposure
Prioritization ensures resources focus on high-impact risks.
3. Mitigation Strategies
Develop strategies to reduce risk, such as:
- Data anonymization and secure pipelines
- Model validation and performance testing
- Human-in-the-loop oversight for critical decisions
- Legal review for content generation
- Responsible AI policies for bias and fairness
Mitigation transforms high-risk areas into controlled, manageable processes.
4. Monitoring & Audit Mechanisms
Continuous monitoring is essential to detect emerging risks:
- Real-time model performance and output tracking
- Periodic audits for compliance adherence
- Alerts for data breaches or misuse
- Documentation and traceability for accountability
Monitoring ensures risks are addressed before they escalate.
5. Governance & Accountability
Establish clear roles and responsibilities:
- Risk Owners: Business or functional leaders accountable for mitigation
- Compliance Leads: Oversee regulatory adherence and audits
- AI Governance Teams: Monitor model behavior and ethical compliance
- Executive Sponsors: Provide oversight and strategic alignment
Strong governance ensures risk is managed consistently across all units.
Integrating Risk Management Into the GenAI Lifecycle
- Planning: Identify risks before model selection or use case deployment
- Deployment: Implement mitigation strategies, secure data pipelines, and human oversight
- Monitoring: Track metrics, incidents, and compliance adherence
- Optimization: Refine models, policies, and workflows based on insights
Integration ensures risk management is proactive, not reactive.
Benefits of a GenAI Risk Management Framework
- Reduced Legal Exposure: Adherence to regulatory and IP requirements
- Operational Resilience: Fewer errors, outages, or inaccurate outputs
- Ethical Compliance: Fair and transparent AI usage
- Scalable Innovation: Safe adoption across departments and geographies
- Trust & Reputation: Confidence among customers, partners, and regulators
Industries Where Risk Management Is Critical
- Banking & Financial Services: Fraud, compliance, and regulatory risk
- Healthcare & Life Sciences: Patient safety, privacy, and regulatory adherence
- Insurance: Ethical underwriting, risk modeling, and fairness
- Retail & E-commerce: IP compliance, content generation, and customer trust
- Manufacturing & Energy: Operational reliability and safety-critical decisions
Partnering to Build a GenAI Risk Management Program
Many enterprises collaborate with GenAI consulting and compliance partners to:
- Assess and categorize risks
- Build governance and compliance frameworks
- Implement monitoring dashboards
- Train employees on safe AI usage
- Ensure regulatory readiness
Partnering accelerates maturity while reducing trial-and-error risk.
From Innovation to Safe, Scalable AI Adoption
Generative ai development services can transform enterprise operations—but only if risks are managed proactively. An Enterprise GenAI Risk Management & Compliance Framework ensures AI initiatives are safe, ethical, and compliant, enabling scalable, sustainable, and high-impact adoption.
FAQs
1. Is risk management mandatory for all GenAI initiatives?
Yes, particularly for enterprise-scale adoption and regulated industries.
2. How often should GenAI risks be reviewed?
Continuous monitoring with periodic reviews (quarterly or bi-annually) ensures early detection of emerging risks.
3. Who should own GenAI risk management?
Ownership is shared across business leaders, compliance teams, AI governance units, and executive sponsors.